Vol 102, No 2 (2025)
- Year: 2025
- Published: 12.05.2025
- Articles: 10
- URL: https://microbiol.crie.ru/jour/issue/view/189
ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
A study of the safety and immunogenicity of a new vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19 based on virus-like particles in phase I clinical trials
Abstract
Introduction. One of the more promising developments in preventing the spread of infections, including COVID-19, is the production of vaccines based on virus-like particles (VLP). Currently, in the National Research Center for Epidemiology and Microbiology named after N.F. Gamaleya of the Ministry of Health of the Russia has developed a VLP-based vaccine against COVID-19.
The aim of this study is to evaluate the tolerability, safety and immunogenicity of a new vaccine for the prevention of COVID–19 based on VLP compared with placebo for 21 days after two intramuscular injections in phase I clinical trials.
Materials and methods. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the tolerability, safety and immunogenicity of a vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19 based on VLP was conducted with a dose of the drug containing 40 and 80 micrograms of antigen, the placebo being 0.9% NaCl. The presence or absence of adverse events (AEs) after vaccination was noted in 180 volunteers aged 18 to 55 years; clinical and biochemical blood parameters, the intensity of humoral and cellular immunity before and after vaccination were assessed using enzyme immunoassay, neutralization reactions, lymphocyte blast transformation reactions and flow cytometry.
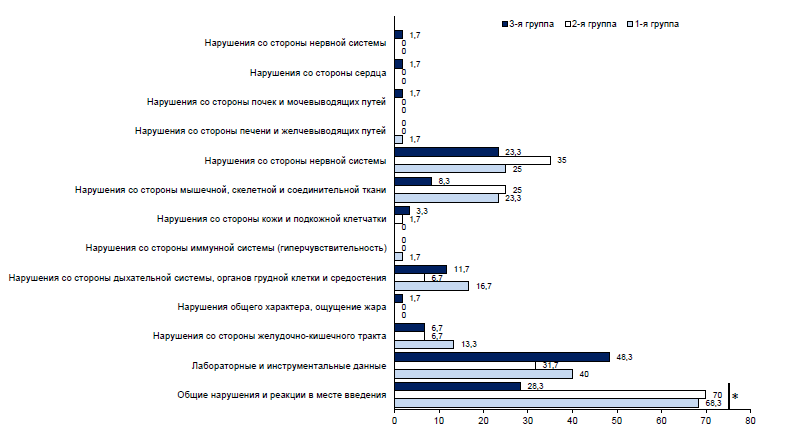
Results. An analysis of the tolerability and safety of the new COVID-19 VLP-vaccine showed that most adverse events were registered within the first 10 days after vaccination, mainly after the first vaccination. In the period from 11 to 21 days after vaccination, AEs were observed in isolated cases. No deaths, serious or other AEs have been reported. The administration of the studied vaccine to the volunteers had no negative effect on the basic vital signs. A comparative analysis of immunogenicity indicators in volunteers showed that the administration of a vaccine with both an antigen content of 40 µg and an antigen content of 80 µg leads to a pronounced and significant increase in the level of specific immunoglobulins, virus neutralizing antibodies and activation of a cell-mediated immune response. As part of the phase I clinical trials, a dose of 80 µg was selected as optimal.
Conclusion. It has been shown that a new vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19 based on VLP with an antigen content of 40 and 80 µg when administered intramuscularly to volunteers does not cause serious adverse events and induces a tense humoral and cellular immune response.
 135-149
135-149


Molecular and biological characterization of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates from patients with pneumococcal meningitis
Abstract
The aim of the study is to provide key characteristics of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates circulating in Russia in 2015–2020 and isolated from pneumococcal meningitis patients based on high-throughput sequencing data, including global pneumococcal sequence clusters, serotypes, virulence factors and genetic determinants of resistance, in comparison with clinical data on antimicrobial susceptibility.
Materials and methods. We studied 68 invasive S. pneumoniae isolates from blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with bacterial meningitis in different regions of Russia in 2015–2020. Species identification was performed taking into account the morphology of colonies on blood agar, the presence of α-hemolysis, negative catalase reaction, sensitivity to optoquine, and positive latex-agglutination results. The sensitivity of isolates to antimicrobials was determined by microdilution in broth, and sensitivity categories were determined based on borderline values of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). Whole genome sequencing of S. pneumoniae isolates, analysis of isolates for penicillin-binding protein signature, determination of global pneumococcal sequence clusters, MLST alleles, serotypes, sequence types and acquired resistance genes (mefA, ermB, tetM, folA/P, cat), identification of virulence genes were carried out.
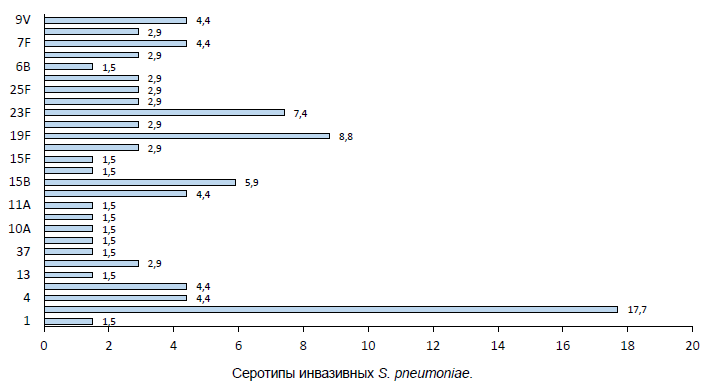
Results. Twenty-eight GPSCs, 45 sequence types and 27 serotypes were identified. The coverage rates of PPV-23 and PCV-13 were 78% and 59%, respectively. Serotypes 3 (18%), 19F (9%), 23F (7%) and 15B (6%) were predominant. The GPSC12 lineage (serotype 3) was predominant (43%). Lineages expressing vaccine serotypes GPSC1(19F), GPSC6(14), GPSC13(6A), GPSC904(14) and GPSC10(19F) exhibited multiple antimicrobial resistance, including penicillin resistance. The resistant lineages expressing non-vaccine serotypes were GPSC230 (13) and GPSC177 (35F). In most cases, genotypic and phenotypic resistance to penicillin (increased MICs of β-lactams correlated with types of penicillin-binding proteins), erythromycin (ermB, mefA, ermB/mefA), clindamycin (ermB) and tetracycline (tetM), and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (folA, folP) was found to be consistent. The virulence genes cbpG, lytA, pce/cbpE, pavA, pfbA, ply, hysA, nanA and cps4A were detected in all isolates. Zinc metalloproteinase C was detected in 13% of isolates.
Conclusion. A high diversity of serotypes and lineages among pneumococcal isolates from meningitis patients was revealed. Out of the 68 S. pneumoniae isolates from patients with bacterial meningitis, more than 17% belonged to non-vaccine serotypes. The results of phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance comparison were characterized by good concordance, which indicates the necessity for further study of the possibility of using whole-genome sequencing as a diagnostic tool to identify resistance mechanisms in clinical isolates of pneumococci.
 150-161
150-161


Humoral immunity to adhesins and toxins of the pertussis pathogen in mice immunized with experimental acellular pertussis vaccines from biofilm and planktonic cultures of Bordetella pertussis
Abstract
Introduction. Whooping cough remains an urgent health problem worldwide, including in countries with high vaccination rates, where, since the 1990s, there has been an increase in the incidence of whooping cough, an increase in the severity of the disease and mortality. In this situation, it is necessary to create a new generation of acellular pertussis vaccines (аPV) that can more effectively affect the colonization, persistence and transmission of Bordetella pertussis. One of the possible directions for improving the vaccine prophylaxis of pertussis infection is the creation of aPV based on protective antigens isolated from biofilm cultures of B. pertussis.
The aim of the study was to research the level of IgG antibodies to the antigens of the pertussis pathogen: adhesins — filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA), pertactin (PRN) and toxins — pertussis toxin (PT), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in mice immunized with experimental aPV based on antigenic complexes (AC) isolated from biofilm and planktonic cultures of B. pertussis.
Materials and methods. Experimental aPV based on AC isolated from the culture medium of biofilm (aPV-B) and planktonic (aPV-P) cultures of B. pertussis strain No. 317 (serotype 1.2.3) were used in the experiments. IgG titers of antibodies to PT, FHA, PRN and LPS in blood sera of mice immunized with aPV-B and aPV-P was determined in ELISA.
Results. The titers of IgG antibodies to adhesins (FHA and PRN) in the aPV-B group were 8 and 4 times higher, respectively, compared with aPV-P, in the absence of significant differences in the titers of IgG antibodies to PT and LPS.
Conclusion. The higher ability of aPV-B to induce an immune response to B. pertussis adhesins compared to aPV-P, in the absence of significant differences between them in stimulating IgG antibodies to toxins, indicates the advantage of using antigenic complexes from biofilm cultures to create aPV of a new type.
 162-167
162-167


Dynamics of enzymatic activity in primary culture of Syrian hamster adherent leukocytes ex vivo infected with SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Introduction. The continued epidemic relevance of SARS-CoV-2, even after the end of the associated COVID-19 pandemic in 2023, necessitates further study of the interaction of this virus with the first line of cellular defense, neutrophils.
The aim of the study was to determine the enzymatic activity of peripheral blood leukocytes of Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) in the dynamics of ex vivo SARS-CoV-2 infection, which characterizes the microbicidal potential of innate immunity cells.
Materials and methods. The SARS-CoV-2/Vladivostok/R-8726/2021 strain was used at infectious doses of 3 lg (TCID50/mL) and 2 lg (TCID50/mL) (TCID50 is the 50% tissue cytopathic dose for the Vero E6 cell line); the contact time of the infecting virus-containing liquid with the cell culture was 1 h. The number of viable cells in the adherent leukocyte culture was counted using an inverted microscope equipped with a digital camera and MCView program. The specific (per 1 viable cell) activities of adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase), 5′-nucleotidase (adenosine monophosphatase, AMPase), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), succinate dehydrogenase (SDH), myeloperoxidase (MPO) and cytochrome oxidase (CCO) were determined spectrophotometrically after incubation with specific substrates of infected and uninfected cell cultures 1, 16, 24, 48 h after virus inoculation.
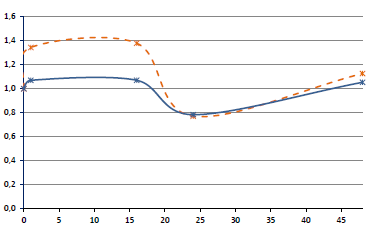
Results. The enzymatic activity of leukocytes 1 h after virus inoculation, compared to uninfected leukocytes, was as follows: specific activity of ATPase, MPO was decreased, activity of AMPase, LDH, SDH was increased; 16 h after virus inoculation, activity of MPO was decreased, activity of AMPase, LDH, SDH was increased, activity of ATPase and CCO was at the initial level, i.e. approximately at the level of the uninfected control; 24 h after virus inoculation, AMPase activity was decreased, ATPase activity was increased, LDH, SDH, MPO, CCO activity was at the initial level; 48 h after virus inoculation, ATPase, LDH, SDH, MPO, CCO activity was increased, AMPase activity was at the initial level. Changes in enzymatic activity depend on the infecting dose and correlate with virus accumulation in the culture medium.
Conclusion. The revealed dynamics of enzymatic activity in the primary culture of adherent leukocytes ex vivo infected with SARS-CoV-2 indicates a decrease in the microbicidal potential of cells of innate immunity in the course of this infection.
 168-178
168-178


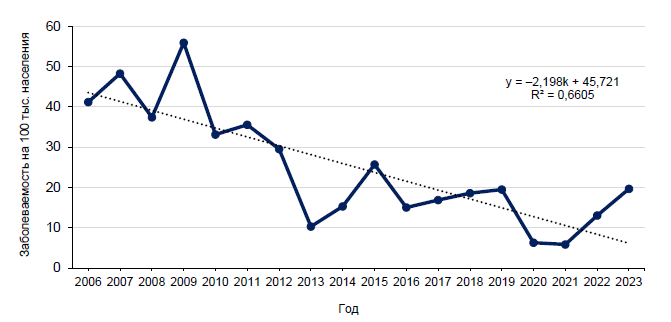
Prediction of the incidence of lyme disease using mathematical modeling methods (using the example of the Kirov region)
Abstract
Introduction. The Kirov region is an endemic region for Lyme disease (ixodic tick-borne borreliosis), which is caused by climatic conditions, an abundance of ticks and their feeders. The economic damage caused by Lyme disease includes the cost of treating patients and eliminating natural foci. Morbidity forecasting is necessary for planning preventive measures (acaricide treatments, awareness-raising activities with the population) and entomological monitoring. The effectiveness of such measures exceeds the above costs, which underlines the relevance of the study.
The aim of the study is to analyze the influence of various factors on the incidence of Lyme disease using mathematical modeling methods for further epidemiological forecasting using the example of the Kirov region.
Materials and methods. The data of the state reports «On the state of sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population in the Kirov region» for 2006–2023 on the incidence of Lyme disease, the first and last reported cases of tick attachment to humans and the volume of acaricide treatments were studied. Hydrometeorological data: monthly and annual averages of air temperature, humidity, and precipitation. Spearman correlation analysis and multiple regression analysis were performed using the «Excel MS Office-2021» and «Statistica Advanced 12 for Windows RU» software. The level of p < 0.05 was chosen as a criterion of statistical significance.
Results. The interval forecast of incidence is up to 18.67 by 2024, 16.51 by 2025, and 14.36 per 100,000 population by 2026. Correlations between climatic factors and morbidity have been identified. A negative reliable correlation of moderate density was revealed between the incidence of Lyme disease in the Kirov region and the volume of acaricide treatments. Two forecasting models have been developed: based on the timing of the first and last reported cases of tick bites; based on hydrometeorological factors and the volume of acaricide treatment.
Conclusion. The incidence of Lyme disease in the Kirov region is characterized by a downward trend. Mathematical models for predicting morbidity in the Kirov region are proposed.
 179-189
179-189


Possibilities and prospects of using biofluorescent proteins at the stage of preclinical evaluation of live vaccines, using the example of the Yersinia pestis vaccine strain EV NIIEG pTURBOGFP-B
Abstract
Introduction. Currently, studies aimed at finding the most informative and optimized method for assessing the survival rate of the plague microbe vaccine strain in the body of animals vaccinated against plague are relevant.
Aim — to evaluate the feasibility of using biofluorescent proteins using the example of the Yersinia pestis vaccine strain EV NIIEG pTurboGFP-B (EVGFP) in combination regimens with immunomodulators at the stage of preclinical evaluation of live vaccines.
Materials and methods. Guinea pigs were immunized with EVGFP grown at 28ºC and 37ºC (EVGFP28 and EVGFP37, respectively), in combination with immunomodulators (azoximer bromide, AB, and human recombinant interferon gamma, HRI).
Results. Fluorescence microscopy revealed seeding (up to 600 m.c. in one field of view) with EVGFP cells at the site of culture introduction in all experimental groups on the 1st day. In vivo flow cytometry showed that on the 1st day in all experimental groups the phagocytic index (PI) averaged 94.5%, with a subsequent decrease by the 4th day by an average of 4.4 times (21.2%). On the 4th day of the study in the EVGFP37+AB group the PI exceeded the similar indicator in the EVGFP37 group by 1.8 times. On the contrary, in the EVGFP28+HRI group the PI decreased by 2.2 times relative to the similar indicator in the EVGFP28 group. In addition, in the EVGFP37+AB and EVGFP37+HRI groups, on day 4, the PI was 2 times higher than in the EVGFP28+AB and EVGFP28+HRI groups, respectively. In the EVGFP37 group, the phagocytic number was on average 1.5 times higher than in the EVGFP28 group.
Conclusion. The obtained data confirm the dependence of the outcome of in vivo interaction of the plague microbe with spleen phagocytes on the temperature of bacterial growth, as well as on the presence of AB and HRI. The use of biofluorescent proteins, as shown by the example of the EVGFP strain and the flow cytometry method, expands the possibilities for assessing live plague vaccines in preclinical studies.
 190-200
190-200


Experience of applying the metagenomic sequencing method on fragments of the 16S rRNA gene for the detection and identification of natural focal infection pathogens
Abstract
Introduction. Metagenomic sequencing is one of the most promising methods for both the detection and identification of natural focal infection (NFI) pathogens and for determining the species composition of various bacterial communities.
The aim is to detect and identify the NFI pathogens in samples of field and clinical material using metagenomic sequencing of 16S rRNA gene fragments, and to analyze the taxonomic composition of endosymbiotic microorganisms in the samples.
Materials and methods. Samples of field (14 samples) and clinical (2 samples) material with varying loads of DNA from NFI pathogens, determined by PCR (Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Francisella tularensis, Rickettsia spp., Coxiella burnetii), were investigated. Amplification of fragments of the gene encoding 16S rRNA was performed using primers flanking the variable regions of the gene.
Results. In 14 out of 16 studied samples, target NFI pathogens were detected. The species identified included R. aeschlimannii (in 57.1% of positive samples), B. valaisiana (in 16.6%), F. tularensis (in 75%), C. burnetii (in 100%), and borreliae — pathogens of relapsing fevers (B. turcica, B. hispanica) were also found in one sample. The taxonomic structure of the microbiome of Ixodes ricinus, Dermacentor reticulatus, Rhipicephalus annulatus, Hyalomma aegyptium, Dermacentor marginatus ticks collected in the southern regions of the Russian Federation was studied. It was shown that the predominant microorganisms are representatives of the genera Flavobacterium, Pseudomonas, Serratia, Aeromonas, Pedobacter, Bradyrhizobium, Shingomonas. DNA markers of microorganisms — endosymbionts of ticks Candidatus Midichloria mitochondrii, representatives of the genera Rickettsiella, Coxiella, non-pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic species of the genus Francisella were found in pools of Ixodes ticks.
Conclusion. The effectiveness of the method of metagenomic sequencing of fragments of the 16S rRNA gene for the detection and identification of NFI pathogens in samples of clinical and field material was demonstrated. Metagenomic sequencing of 16S rRNA gene regions can be recommended as an additional laboratory method for detecting and identifying NFI pathogens.
 201-212
201-212


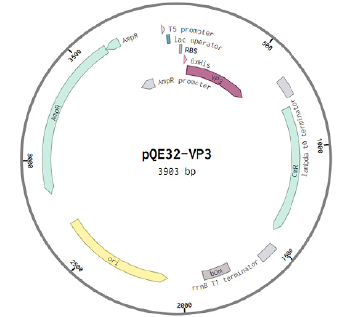
Production and purification of recombinant proteins VP2 and VP3 of the Alongshan virus of the Jingmenvirus group and evaluation of their immunochemical properties
Abstract
Introduction. Alongshan virus is a representative of the unclassified group of Jingmenviruses (Flaviviridae), which is detected in Ixodes persulcatus, Ixodes ricinus ticks and various mosquito species in Russia, China, Finland and France. Unlike traditional orthoflaviviruses, the Alongshan virus genome is represented by 4 positive-sense RNA segments. The first and third segments of the genome encode proteins homologous to proteins of the replicative machinery of orthoflaviviruses, the remaining segments encode putative structural proteins that have no known homologues: segment 2 — VP1a (envelope protein), VP1b and NuORF; segment 4 — VP2 (capsid) and VP3 (membrane). Human cases of Alongshan virus-associated disease have been described.
The aim of this study is to develop a system for expression and purification of recombinant VP2 and hydrophilic site VP3 proteins to test their antigenic properties.
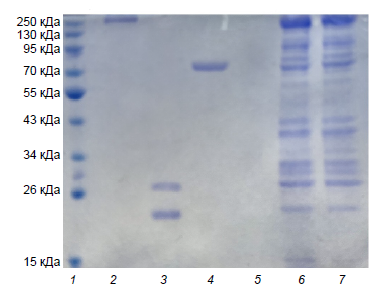
Materials and methods. Miass527 strain of Alongshan virus was used to produce hyperimmune mouse sera and recombinant proteins in a bacterial expression system. Bioinformatic analysis of sequences encoding target proteins and genetically engineered cloning were carried out in this study. Western blotting and enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) were performed to control the results.
Results. Recombinant proteins of Alongshan virus have been used in a laboratory diagnostic test system to determine the presence of antibodies to the virus. The obtained recombinant VP2 protein is able to detect antibodies in all tested sera of infected mice, as well as antibodies in human sera both in Western blotting and in enzyme immunoassay. At the same time, antibodies to the recombinant region of VP3 protein were detected irregularly in antiviral immune sera.
Conclusion. The detection of antibodies to Alongshan virus in patients confirms the necessity for further investigation of this group of viruses.
 213-222
213-222


SCIENCE AND PRACTICE
Streptococcal effective molecules as promising antiсancer agents: pros and cons
Abstract
Oncological diseases remain the main cause of death and disability of the population worldwide. The most malignant types of cancer include of pancreas, liver and brain tumors. Modern methods of therapy (including chemoradiation, targeted and immune therapy) do not allow achieving the desired effectiveness in this group of patients. In this regard, new approaches to the treatment of oncological diseases are needed.
The aim of this review was to discuss the mechanisms of anticancer action of Strepococcus pyogenes and other streptococcal species, as well as to consider their cancer-stimulating effects and their limitations.
The review considers the current state of the problem of using bacterial oncotherapy involving streptococci A group (in particular, S. pyogenes). The involvement of S. pyogenes pathogenicity factors is discussed: M-protein, exotoxins: streptolysins S, O, superantigens, arginine deiminase, etc., as well as molecular mechanisms mediated by the host immune system cells. The authors' own data show that S. pyogenes exhibits selective M-protein-mediated cytolytic activity against C6 glioma and pancreatic adenocarcinoma (Panc) tumor cells and no activity against normal fibroblasts. The data on preclinical and clinical application of the streptococcal-based medicine OK-432 for the therapy of oncological diseases are briefly summarized. Tumor-associated properties of streptococci (induction of cytokine storm, proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of vascular epithelial cells, formation of neutrophil extracellular traps in the tumor microenvironment) caused by their interaction with immune cells of the tumor-bearing organism are also discussed.
Conclusion. The research data presented in this review convincingly demonstrate that S. pyogenes, with the participation of pathogenicity factors, can directly exert an antitumor effect on cancer cells. However, it should be noted the streptococcal vaccine should be used with caution, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient's immune system, since S. pyogenes can also have effects of the opposite nature, requiring further research.
 223-238
223-238


REVIEWS
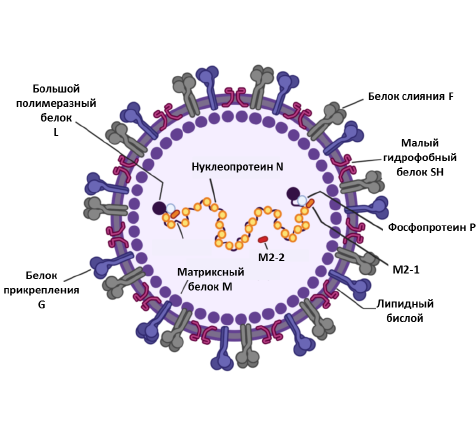
Current status of developments in the field of respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
Abstract
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the leading cause of upper respiratory tract infections in children and the elderly. The only specific treatment approved for RSV is the monoclonal antibody Palivizumab for passive immunoprophylaxis in high-risk infants. Sixty years after the virus was discovered, several safe RSV vaccine candidates have been licensed. This was facilitated by research to identify the structure of RSV, to study the basic functions of RSV components as well as the mechanisms of innate and acquired immune responses to infection. The negative result of a clinical trial of formalin-inactivated RSV vaccine in children, which resulted in the death of several vaccinated individuals, was taken into account.
The aim of the study was to summarize data from studies of RSV vaccine candidates in laboratory animals and in clinical trials on different age groups.
Articles for the analysis of preclinical and clinical trials of RSV vaccines were found, using the PubMed search engine with “respiratory syncytial virus and vaccine” as the keywords. The selection criteria were that original articles should contain information on preclinical and clinical studies, the latter including phase I–IV randomized controlled trials. From 1967 to the present year, 296 articles summarizing data from studies of RSV vaccine candidates and 1788 articles summarizing data from animal trials of vaccine candidates were found. The review summarizes data from preclinical studies of vaccine candidates and their developers, vaccine formulations, animal models on which the studies were conducted, as well as a brief description of the main findings. Data on clinical trials of vaccine candidates are presented, including target populations, clinical trial number and sources where the results of these trials were published.
 239-264
239-264