Vol 98, No 2 (2021)
- Year: 2021
- Published: 05.05.2021
- Articles: 16
- URL: https://microbiol.crie.ru/jour/issue/view/43
Full Issue
ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
Application of ultrafiltration membranes for purification and concentration of Sabin poliovirus type 1
Abstract
Introduction. Since the development of inactivated polio vaccines, different stages of the production process have been changed and improved. Current production of inactivated polio vaccines based on both wild and attenuated strains includes several technological stages, one of which is the concentration of the virus-containing liquid, which ensures poliovirus concentration, and purification of the virus-containing liquid from a significant part of the ballast components.
Research objective is to compare the characteristics of ultrafiltration membranes and select the membranes that provide optimal value of purification and concentration of poliovirus type 1 (Sabin strain).
Materials and methods. Laboratory ultrafiltration systems from two manufacturers with 50, 100, and 300 kDa membranes were used for the concentration. Results were evaluated by the content of total protein, which is the main stress for the subsequent purification stages, the value of infectious virus titer in the concentrate, and the content of D-antigen as the target product.
Results and discussion. Obtained results demonstrated that the content of the target product (the highest D-antigen content) and purification from impurity proteins (the total protein content in the concentrate) were most optimal when a membrane with a cut-off of 300 kDa was used for concentration. The study also evaluated the real cut-off components by various membranes to determine the composition of the protein load on the target product.
Conclusion. In terms of quality of the resulting target product and the manufacturability of the production process, the use of a 300 kDa membrane is the most appropriate when working out the technology for manufacturing inactivated polio vaccine based on Sabin strains of poliovirus and the Vero line as a producing culture.
 135-143
135-143


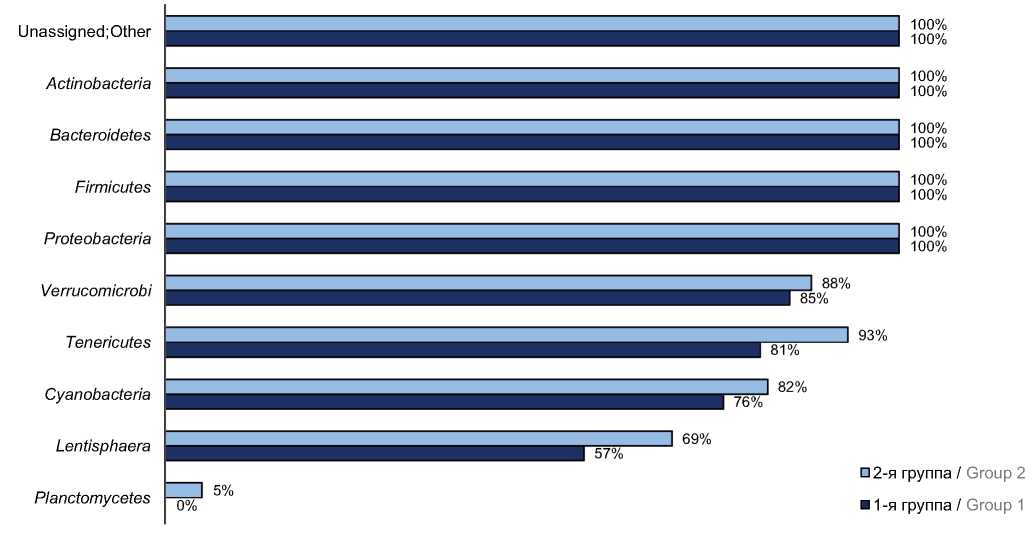
Characteristics of the colonic microbiome in patients with different obesity phenotypes (the original article)
Abstract
Introduction. The concept of heterogeneity in obesity depending on the risk of developing cardiometabolic complications has garnered attention in recent decades, since not everyone with obesity goes on to develop metabolic dysfunction.
The aim of the work is to study specific characteristics of colonic microbial communities in patients with different obesity phenotypes and in healthy individuals by employing metagenomics methods.
Materials and methods. A total of 265 individuals (44 men and 221 women; mean age 47.1 ± 4.8 years) were enrolled in the study. They were further divided into clinical groups: Healthy normal-weight individuals (n = 129); patients with obesity (n = 136), including metabolically healthy obesity (n = 40) and metabolically unhealthy obesity (n = 55). Quantitative and qualitative assessment of the intestinal microbiome was based on metagenomic analysis. Fecal samples were used to isolate DNA and perform sequencing of the variable v3-v4 region of the 16S rRNA gene.
Results. The study revealed statistically significant (p < 0.05) differences between quantitative and qualitative variables in studied phylotypes of colonic microorganisms in healthy individuals without obesity and in patients with different obesity phenotypes.
Discussion. Patients with obesity had higher levels of Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria and lower levels of Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, TM7 (Saccharibacteria), Fusobacteria, and more frequently detected phyla Tenericutes, Planctomycetes and Lentisphaerae compared to healthy individuals. Metabolically healthy obese patients had more rarely detected phylum Lentisphaerae in their colonic microbiome, increased numbers of Firmicutes and reduced numbers of Bacteroidetes compared to metabolically unhealthy obese patients.
Conclusion. The findings demonstrate alterations in the colonic microbiome in patients with different obesity phenotypes.
 144-155
144-155


Influence of immunomodulation on intracellular cytokine expression by spleen T-helpers of mice immunized by Yersinia pestis EV NIIEG
Abstract
Aim. To characterize the intracellular expression of cytokines by spleen T-helpers and the spontaneous production of cytokines in the blood of BALB/c mice immunized with Yersinia pestis EV NIIEG against the background of immunomodulation.
Materials and methods. Intracellular expression of CD4+IFN-γ+, CD4+IL-4+, CD4+IL-17+ was determined in mice spleen cell suspensions by flow cytometry, IFN-γ and IL-10 were measured in ELISA in blood supernatants on day 3 and day 21 after the immunization with Y. pestis EV against the background of immunomodulation. On day 21 after the immunization animals were infected by Y. pestis 231 at a dose of 400 LD50.
Results. Differences in cytokine response to studied drugs, correlated with CD4+IFN-γ+ levels in animals, were identified. On day 3, a significant decrease in CD4+IFN-γ+ was observed in response to Y. pestis EV and to recombinant gamma interferon (Ingaron). A significant increase in CD4+IFN-γ+ was detected in response to vaccine strain administered with azoximer bromide (Polyoxidonium). Intracellular expression of IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-17 increased on day 21by an average of 2,3 times when immunomodulators were used in the immunization schedule. In addition, on day 21 a significant (p ˂ 0.05) increase in the proportion of T-helpers expressing IFN-γ, as well as in level of spontaneous IFN-γ production in blood supernatants was observed only in animals immunized by schedules that included immunomodulators. After the challenge with Y. pestis 231 of animals previously immunized by schedules that included Polyoxidonium, the correlation analysis confirmed the association (r = 0,94; p = 0,0004) of mice survival with intensity of CD4+IFN-γ+ expression.
Conclusion. The data obtained confirm the effectiveness of Polyoxidonium application in experimental animal Y. pestis EV immunization schedule and the usefulness of intracellular cytokine expression measurement for assessment of the level of protection following the immunization.
 156-162
156-162


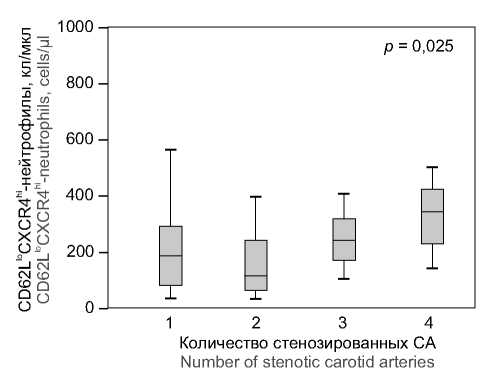
Association of the increased circulating CD62LloCXCR4hi neutrophil count with carotid atherosclerosis
Abstract
Introduction. The role of neutrophils in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis as well as in the development of its complications has received scientific attention only in the recent years. Today, there is growing evidence to support a role of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in sustained inflammation during different chronic inflammatory diseases by retaining neutrophils at inflammatory sites.
The aim of the study is to assess the diagnostic and prognostic significance of circulating CD62LloCXCR4 hi neutrophils in patients with carotid atherosclerosis.
Materials and methods. A total of 75 patients (52% of men and 48% of women) aged 40 to 64 years were examined. None of them were diagnosed with atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. All the patients underwent carotid artery duplex scanning. The flow cytometry and CD16, CD11b, CD62L, CD182 (CXCR2) and CD184 (CXCR4) conjugated monoclonal antibodies were used for phenotyping and differentiation of neutrophil subpopulations.
Results. Atherosclerotic plaques in carotid arteries were detected in 72% of the patients; most of the patients were diagnosed with stenosis development in more than one of the carotid arteries (CA). The elevated levels of circulating CXCR4h neutrophils were associated with the levels of total cholesterol (r = 0.377; p = 0.001), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (r = 0.293; p = 0.014) and triglycerides (r = 0.388; p = 0.003). The study revealed direct correlation between the circulating CXCR4 hi neutrophil count and the cumulative percentage of CA stenosis (r = 0.300; p = 0.011), including the number of stenosed CA (r = 0.291; p = 0.034). It was also found that CXCR4 hi neutrophil counts demonstrated a statistically significant increase along with the increased number of stenosed CA (p = 0.025). The ROC analysis findings show that the elevated CXCR4 hi neutrophil counts ≥260 cells/μL made it possible to diagnose stenotic lesion of 4 CAs with a sensitivity of 71.4% and specificity reaching 76.6%.
Conclusion. In patients with carotid atherosclerosis, the increased count of circulating CD62LloCXCR4 hi neutrophils was associated with the increased number of stenosed CAs, while no significant changes were observed in the other examined subpopulations of neutrophil granulocytes. The increased CD62LloCXCR4 hi neutrophil count made it possible to diagnose stenotic lesion of 4 CAs with a sufficient sensitivity and specificity.
 176-183
176-183


Results of cholera monitoring in administrative territories of Russia from 2013 to 2019
Abstract
Purpose. A dynamic comparative analysis of the results of identification of Vibrio cholerae (V. cholera) isolates from water and human specimens isolated during the monitoring of cholera throughout the Russian Federation in 2013–2019.
Materials and methods. Total 385 strains of V. cholerae O1 serogroup (including one toxigenic V. cholerae O1 El Tor Inaba — Rostov region, 2014) and the R-variant from environment objects were identified in the territory of 21 regions of the Russian Federation.
Results. It was found that 91% of the strains were isolated in 7 regions of the Russian Federation: Republic of Kalmykia, Krasnodar Krai, Transbaikal Krai, Khabarovsk Krai, Primorsky Krai, Rostov region and Irkutsk region. 2.3% of strains were atypical in their agglutinability, and 75.3% of strains had atypical phagosensitivity. Phagotypes were identified for 13.2% of strains isolated in 11 administrative territories. Phageotype 11 included 48.8% of the strains isolated mainly in the Transbaikal Krai. Non-toxigenic strains of V. cholerae nonО1/nonO139 (n = 46) were isolated from 43 patients with acute intestinal infections and otitis in 8 regions of Russia. PCRtyping of 377 non-toxigenic V. cholerae strains demonstrated that they belong to 13 clusters and 71 genotypes. Strains with unique genotypes (probable cases of importation) and with the same genotypes repeatedly isolated in different years in one or several territories of the Russian Federation were identified, indicating the prevalence of strains in environment throughout the country.
Conclusion. The results allowed us to characterize the epidemiological situation of cholera in Russia (in terms of the environment contamination with V. cholerae O1) as unstable, but not significantly changed over the past 7-year period. These data are important for substantiating the forecast for further development of the epidemiological situation.
 163-175
163-175


Ten-year monitoring of sensitization to house dust mites
Abstract
Statistical studies of patients' sensitization to allergens make it possible to form a general picture of sensitization for the whole country, help doctors to develop competent tactics for examining patients in the regions and can be used for the development of new formulations of allergy vaccines.
Objective. To study the sensitization to inhalation allergens Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Der. p.) and Dermatophagoides farinaе (Der. f.) in Moscow and the Moscow region in 2010–2019 and to identify the structure, features and dynamic changes in sensitization to Der. p. and Der. f. based on the analysis of the allergosensitivity profile of patients with IgE-mediated allergic diseases (IgEA).
Materials and methods. Blood serum samples of Moscow and the Moscow region residents with IgEA (n = 2849) were examined by RIDA AllergyScreen method in 2010–2019.
Results. According to the results of the study spanning the last ten years, about 18–21% of patients with IgEA in Moscow and the Moscow region have sensitization to Der. p. and/or Der. f. There was a statistically significant decrease in sensitization to Der. p. from 2017 to 2019. House dust mites of the type Der. f. more often cause a higher level of sensitization compared to Der. p.
Discussion. The data obtained indicate the change in the sensitization of patients to Pyroglyphidae, namely Der. p. against the background of changes in the housing acarocomplex of Moscow and the Moscow region. Features of protein molecules of these species of dust mites may contribute to their varying degrees of the impact on immunological reactivity in the population studied.
Conclusions. The decrease in the prevalence of Der. p. is most likely accounted for the changes in the ecosystem of homes of residents of Moscow and the Moscow region.
 184-189
184-189


DISCUSSIONS
Contemporary strategy to control viral hepatitis A in the Russian Federation
Abstract
The problem of choosing a strategy to control hepatitis A in the Russian Federation remains relevant for the health care of our country. By strategy we mean a scientifically based program of action that defines the priorities and resources needed to effectively control hepatitis A.
The aim of the work is to present a strategy to control hepatitis A in the Russian Federation, taking into account the realities of today. Based on the analysis of Russian and international studies, we present answers to the questions that should be addressed before the choosing a strategy to control hepatitis A in the Russian Federation. The low incidence of hepatitis A creates a false image of the favorable situation with this infection. The rationale is given to include vaccination against hepatitis A in the National Vaccination Schedule in the section of mandatory vaccinations. Routine vaccination of children aged 24 and 36 months will lay the foundation for future protection against this infection. We consider the creating a National Hepatitis A Vaccination Program as an important aim. The implementation of such a program will allow full control of hepatitis A in the Russian Federation.
 190-197
190-197


REVIEWS
Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the interleukin-1 superfamily members: аssociation with viral hepatitis B and C
Abstract
The review provides information on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes encoding some interleukins belonging to the interleukin-1 (IL-1) superfamily and on their association with different infectious and non-infectious human diseases. It also briefs on the history of SNP discovery and the progress in the related scientific studies till the present time. It gives an insight into some mechanisms of interaction between infectious agents and the human immune system, involving SNPs in some cytokines of the IL-1 superfamily. The review provides data on relationships of SNPs in genes encoding other factors of the immune system, which are associated with the specific characteristics of natural history of chronic hepatitis B and C. It explores the significance of assessment of the SNP-proportion in proinflammatory cytokines and their antagonists of the IL-1 superfamily among the healthy population as well as the ratio of individual SNPs in specific groups of patients as a monitoring parameter for epidemiological surveillance of infectious diseases.
 198-212
198-212


Favipiravir: the hidden threat of mutagenic action
Abstract
The antiviral drug favipiravir (FVP), which is a structural analogue of guanosine, undergoes chemical transformation in infected cells by cellular enzymes into a nucleotide form — favipiravir ribose triphosphate (FVPRTP). FVP-RTP is able to bind to viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and integrate into the viral RNA chain, causing a significant mutagenic effect through G→A and С→U transitions in the viral RNA genome. Besides the virus inhibiting effect, the increased synthesis of mutant virions under the action of FPV possess a threat of the emergence of novel threatening viral strains with high pathogenicity for humans and animals and acquired resistance to chemotherapeutic compound. There are three ways to minimize this mutagenic effect of FP. (1) Synthesis of new FPV modifications lacking the ability to integrate into the synthesized viral RNA molecule. (2) The combined use of FPV with antiviral chemotherapeutic drugs of a different mechanism of action directed at various viral and/or host cell targets. (3) Permanent application of high therapeutic doses of FPV under the strict medical control to enhance the lethal mutagenic effect on an infectious virus in the recipient organism to prevent the multiplication of its mutant forms.
 213-220
213-220


Dysbiosis of intestinal microbiota in autism spectrum disorders: new horizons in search for pathogenetic approaches to therapy. Part 2. Gut–brain axis in pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorders
Abstract
The second part of the literature review on the role of intestinal microbiota disturbances in the pathogenesis of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) is devoted to the analysis of published literature on the possible mechanisms underlying the impact of intestinal dysbiosis on the function of the central nervous system and symptoms of ASD and vice versa, the effect of the nervous system on the intestinal microbiota. The hypotheses of slow inflammation, hyperserotoninemia, the production of toxic metabolites of the intestinal microbiota, impaired intestinal wall permeability, and the effect of intestinal dysbiosis on the synthesis of amino acids, vitamins and other biologically active substances that are potentially involved in the etiology and pathogenesis of ASD are considered. Available to date experimental and clinical data supporting these hypotheses are presented. The main mechanisms of the so-called gut-brain axis, which may be related to the pathogenesis of ASD, are formulated.
 221-230
221-230


Ricketsioses in the Lower Volga region
Abstract
The aim of this work was to describe the features of the epidemiology and clinic of rickettsioses at the Lower Volga region.
Materials and methods. Scientific papers on searchable electronic databases (Web of Science, PubMed, eLIBRARY and ResearchGate) were selected and analyzed. Of the 256 found sources, the authors selected 87, taking into account the keywords, after an analysis of the selected literature, 30 sources were included in the present study in accordance with the topic of the work.
Results. On the territory of the Lower Volga region, including the Astrakhan region, two rickettsioses are recorded: rickettsiosis from the tick-borne spotted fevers group — Astrakhan spotted fever (APL) and Q fever (coxiellosis). APL is a relatively new rickettsiosis common in the Caspian Sea basin, along the floodplain of the river Volga to Volgograd, capturing the steppes of Kalmykia. Q fever is recorded in many countries of the world, and in Russia, in terms of its importance and distribution, it occupies one of the first places among endemic diseases. The clinical characteristics of these rickettsioses are also presented.
Conclusions. The study of the epidemiology and clinic of rickettsial infections remains relevant.
 231-238
231-238


BOOK REVIEW
 239
239


 240-241
240-241


OBITUARIES
 242
242


 243
243


 244-246
244-246