Том 99, № 1 (2022)
- Год: 2022
- Выпуск опубликован: 10.03.2022
- Статей: 13
- URL: https://microbiol.crie.ru/jour/issue/view/48
Весь выпуск
ОРИГИНАЛЬНЫЕ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ
Молекулярно-генетические особенности ротавирусов группы А, выявленных в Москве в 2015–2020 гг.
Аннотация
Цель работы — анализ генетических характеристик штаммов ротавирусов группы А (РВА), циркулировавших в Москве в 2015–2020 гг., включая редкие штаммы, нетипируемые методом полимеразной цепной реакции (ПЦР).
Материалы и методы. Исследовали 289 фекальных образцов от детей в возрасте от 1 мес до 17 лет, госпитализированных с острым гастроэнтеритом. Выявление ротавирусов в образцах проводили методами иммунохроматографии и обратной транскрипции (ОТ) с ПЦР в реальном времени (ОТ-ПЦР-РВ). Секвенирование ротавирусного генома проводили по Сэнгеру и методом нанопорового секвенирования.
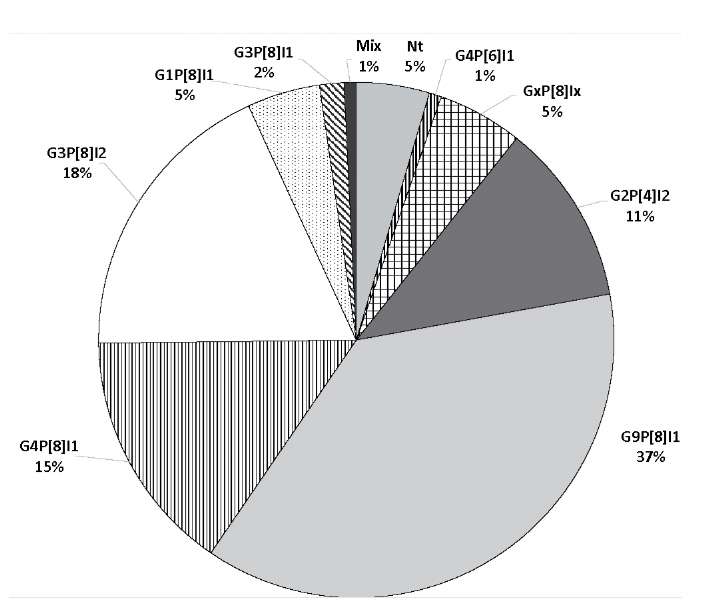
Результаты и обсуждение. В 131 клиническом образце была выявлена РНК РВА, в 125 случаях из них был установлен G/[P]-генотип. В общей структуре преобладали штаммы РВА с генотипом G9P[8]I1 (37%), за ними следовали варианты G3P[8]I2, G4P[8]I1, G2P[4]I2, G1P[8]I1 и G3P[8]I1 (18, 15, 11, 5 и 2% соответственно). Семь (5%) изолятов были идентифицированы как GxP[8]. В 2015–2020 гг. в регионе снизилась частота встречаемости генотипа G4P[8]I1 (с 39 до 9%) и выросла доля генотипа G9P[8]I1 (с 6 до 37%) по сравнению с 2009–2014 гг. В 2018–2020 гг. выявлена высокая доля не встречавшегося ранее DS-1-подобного реассортантного штамма G3P[8]I2, широко распространившегося в мире в последние годы, Методом нанопорового секвенирования проведён анализ генома штамма G3P[8]I2 и редкого штамма G4P[6]I1. Для штамма G4P[6]I1 установлена тесная филогенетическая связь с ротавирусами свиней.
Заключение. За последние годы в генетической структуре РВА, циркулирующих на территории московского региона, произошли существенные изменения. Полученные результаты свидетельствуют о необходимости постоянного мониторинга ротавирусной инфекции и выборочного секвенирования генов РВА для уточнения данных типоспецифической ОТ-ПЦР-РВ. Из-за постоянных изменений генетического состава циркулирующих штаммов РВА требуется периодическая оптимизация систем генотипирования РВА на основе ОТ-ПЦР-РВ.
 7-19
7-19


Генетическое разнообразие и мутации лекарственной устойчивости ВИЧ-1 в Ленинградской области
Аннотация
Введение. Проблема распространения вируса иммунодефицита человека первого типа (ВИЧ-1) к настоящему времени обрела общемировое значение и фактический статус пандемии. В Санкт-Петербурге — крупном транспортном, туристическом, культурном, промышленном и приграничном центре — наблюдается высокая миграционная активность населения. Это может способствовать заносу и распространению новых генетических вариантов вируса, а также рекомбинационным процессам в вирусной популяции Санкт-Петербурга и Ленинградской области.
Цель — охарактеризовать современный субтипический профиль и мутации лекарственной устойчивости ВИЧ-1 среди пациентов с вирусологической неэффективностью антиретровирусной терапии (АРТ) в Ленинградской области.
Материалы и методы. В ходе работы в 2016–2018 гг. был исследован клинический материал от ВИЧ-инфицированных лиц из Ленинградской области с подтверждённой вирусологической неэффективностью АРТ. Для оценки генетического разнообразия и структуры мутаций лекарственной устойчивости полученных изолятов ВИЧ-1 проводили анализ нуклеотидных последовательностей фрагмента гена pol вируса, включающего области, кодирующие протеазу и участок обратной транскриптазы.
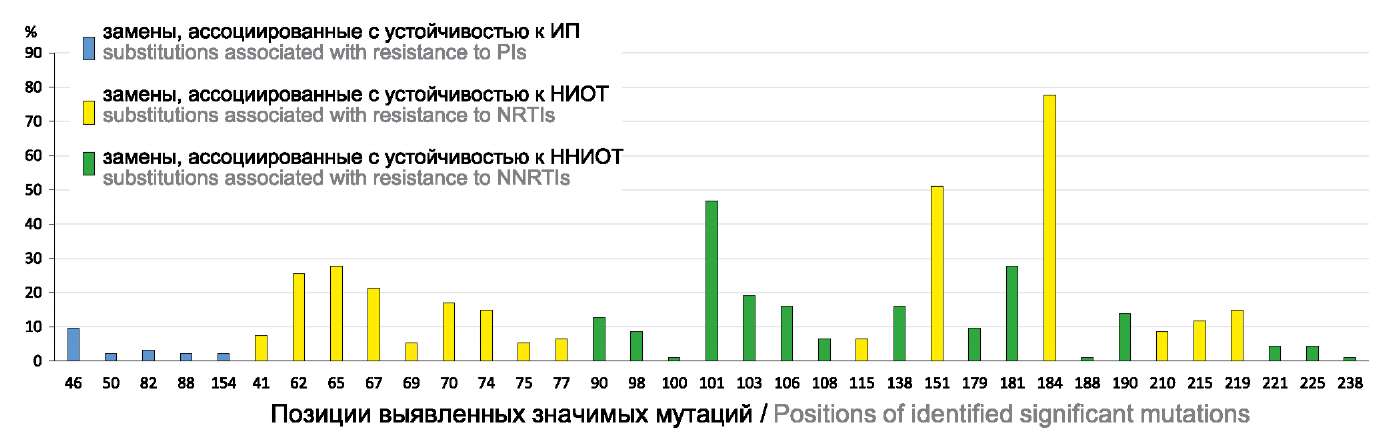
Результаты. В обследованной группе (n = 138) преобладал характерный для России субсубтип A6 (97,4%), однако в единичных случаях были обнаружены субтип В и рекомбинант, образованный циркулирующей рекомбинантной формой CRF_03AB и субсубтипом А1. По результатам анализа у 95,79% пациентов выявлена хотя бы одна значимая мутация лекарственной устойчивости, чаще всего (73% случаев) вирус был устойчив к 2 классам антиретровирусных препаратов, но иногда (8% случаев) — к 3 классам. Всего были определены 105 различных мутаций фармакорезистентности в 35 позициях генома вируса.
Выводы. Учитывая высокую встречаемость мутаций фармакорезистентности ВИЧ-1 у пациентов с вирусологически неэффективной АРТ, представляется необходимым надзор за лекарственной устойчивостью вируса как у получающих АРТ, так и у АРТ-наивных лиц.
 28-37
28-37


Анализ факторов риска, определяющих проявление эпидемического процесса ВИЧ-инфекции в пенитенциарной системе
Аннотация
Введение. В Тюменской области уже более 10 лет отмечается устойчиво высокий уровень поражённости ВИЧ-инфекцией. Особняком среди рисковых групп по заражению ВИЧ стоит группа заключённых под стражу лиц. В обозначенной группе максимально сосредоточены потребители наркотических веществ, мужчины, имеющие половой контакт с мужчинами, работники коммерческого секса. Болезни, приобретённые в период отбывания срока наказания либо усугубившиеся в условиях лишения свободы, становятся проблемой не только освободившихся заключённых, но и сообщества за пределами пенитенциарной системы. С эпидемиологической точки зрения считается принципиально важным выявление в среде осуждённых лиц факторов, способствующих прогрессированию ВИЧ-инфекции с учётом их неравноценного значения среди заключённых и гражданского населения.
Цель исследования — выявление и оценка совокупности факторов риска, определяющей развитие эпидемического процесса ВИЧ-инфекции в зоне высокой концентрации групп риска.
Материалы и методы. Применены методы эпидемиологического исследования, метод логистической регрессии пошагового включения.
Результаты. Наиболее сложная эпидемиологическая ситуация в местах лишения свободы в части выявления случаев ВИЧ-инфекции и поражённости ВИЧ среди осужденных обозначилась с 2008 г. При этом эпидемиологическую обстановку ухудшали и высокие показатели смертности ВИЧ-инфицированных. При проведении исследования нами установлено, что вероятность летального исхода у осуждённых, инфицированных ВИЧ, ассоциирована с совокупностью параметров: мужской пол, парентеральный (наркотический) путь заражения ВИЧ, наличие сопутствующего заболевания — вирусного гепатита и заболевания органов грудной клетки.
 20-27
20-27


Разнообразие субтипов, филогенетический анализ и изучение лекарственной устойчивости штаммов ВИЧ-1, циркулирующих в Уральском федеральном округе
Аннотация
Введение. Уральский федеральный округ (УФО) является одной из наиболее эпидемически неблагополучных территорий в Российской Федерации по ВИЧ-инфекции на протяжении последних 20 лет. Общее число лиц, живущих с ВИЧ/СПИД (ЛЖВС), получающих антиретровирусную терапию (АРТ), превышает 100 тыс. человек (61,7% от всех ЛЖВС в УФО), что создаёт предпосылки для широкого распространения резистентных штаммов.
Целью исследования явились определение субтиповой структуры ВИЧ, оценка генетической гетерогенности выделенных штаммов ВИЧ, анализ распространённости мутаций лекарственной устойчивости (МЛУ) ВИЧ к антиретровирусным препаратам (АРВП) и частоты выявления резистентности к АРВП у лиц, получающих АРТ в УФО.
Материалы и методы. Обследованы 223 пациента на 3–4-й стадии ВИЧ-инфекции, проживающие на территории УФО. Для определения субтипов и МЛУ в гене pol ВИЧ-1 проведены молекулярно-генетические исследования с применением тест-системы «АмплиСенс® HIV-Resist-Seq» методом секвенирования по Сэнгеру на анализаторе «Applied Biosystems 3500». Генетическую гетерогенность оценивали с помощью расчёта идентичности участка генома выделенных штаммов в сравнении с геномами зарубежных штаммов ВИЧ, а также с использованием филогенетического анализа.
Результаты. В изучаемой группе пациентов идентифицированы 5 субтипов ВИЧ-1: субтип A6 встречался в 91,03% случаев, субтип B — в 2,69%, на 3 рекомбинантных субтипа (CRF03_A6B, CRF02_AG, CRF63_02A6) пришлось 6,28%. Среди выделенных штаммов ВИЧ 43,9% имеют большое генетическое сходство (идентичность не менее 97%) со штаммами, выделенными от пациентов из стран ближнего зарубежья (Беларусь, Казахстан, Кыргызстан, Узбекистан, Литва); 35,9% сходны со штаммами, выделенными от пациентов из стран дальнего зарубежья (США, Китай, Южная Корея, Австралия, Швеция, Германия). Установлена высокая гетерогенность генетических вариантов штаммов ВИЧ, циркулирующих на территории УФО, что является неблагоприятным фактором для диагностики резистентности и лечения ВИЧ. Наиболее распространены МЛУ одновременно к нуклеозидным и ненуклеозидным ингибиторам обратной транскриптазы, выявленные в 81 (36,3%) образце. МЛУ M184V, формирующая резистентность к НИОТ, встречалась чаще других (p = 0,0008) и была выявлена в 88 (39,5%) образцах.
Заключение. В субтиповой структуре ВИЧ доминирующим субтипом являлся субтип A6, наиболее распространённый в странах, ранее входивших в состав СССР. Генетическая гетерогенность штаммов ВИЧ, циркулирующих в УФО, позволяет предполагать продолжающиеся заносы ВИЧ-инфекции в УФО из популяций, находящихся за пределами России. Полученные результаты подтверждают высокую распространённость МЛУ (62,8%) и лекарственной устойчивости ВИЧ-1 (60,1%) среди лиц с ВИЧ/СПИД, проживающих на территории УФО. При этом резистентность высокого уровня выявлена у 56,5% пациентов, что требует увеличения охвата лиц, живущих с ВИЧ, обследованием на резистентность ВИЧ, в том числе внедрения мониторинга за первичной резистентностью, в целях оптимизации схем АРТ первой линии.
 38-53
38-53


Роль полиморфизма гена eNOS в иммунопатогенезе первичной открытоугольной глаукомы
Аннотация
Введение. Патологии органа зрения (кератиты, глаукома и др.) занимают ведущее место среди причин снижения зрения и слепоты. По данным литературы, иммунопатогенез бактериальных кератитов связан с активацией макрофагов и кислородным взрывом. Не до конца понятна роль этих механизмов в патогенезе первичной открытоугольной глаукомы. Есть единичные работы, в которых связывают развитие этой патологии с оксидом азота NO, который продуцируется эндотелиальной NO-синтазой (eNOS). Однако, несмотря на многочисленные исследования, роль иммуногенетических в патогенезе глаукомы остаются недостаточно исследованными.
Цель работы — изучение роли полиморфных маркеров T786C, C774T, Glu298Asp гена eNOS при развитии ПОУГ у жителей Пермского края.
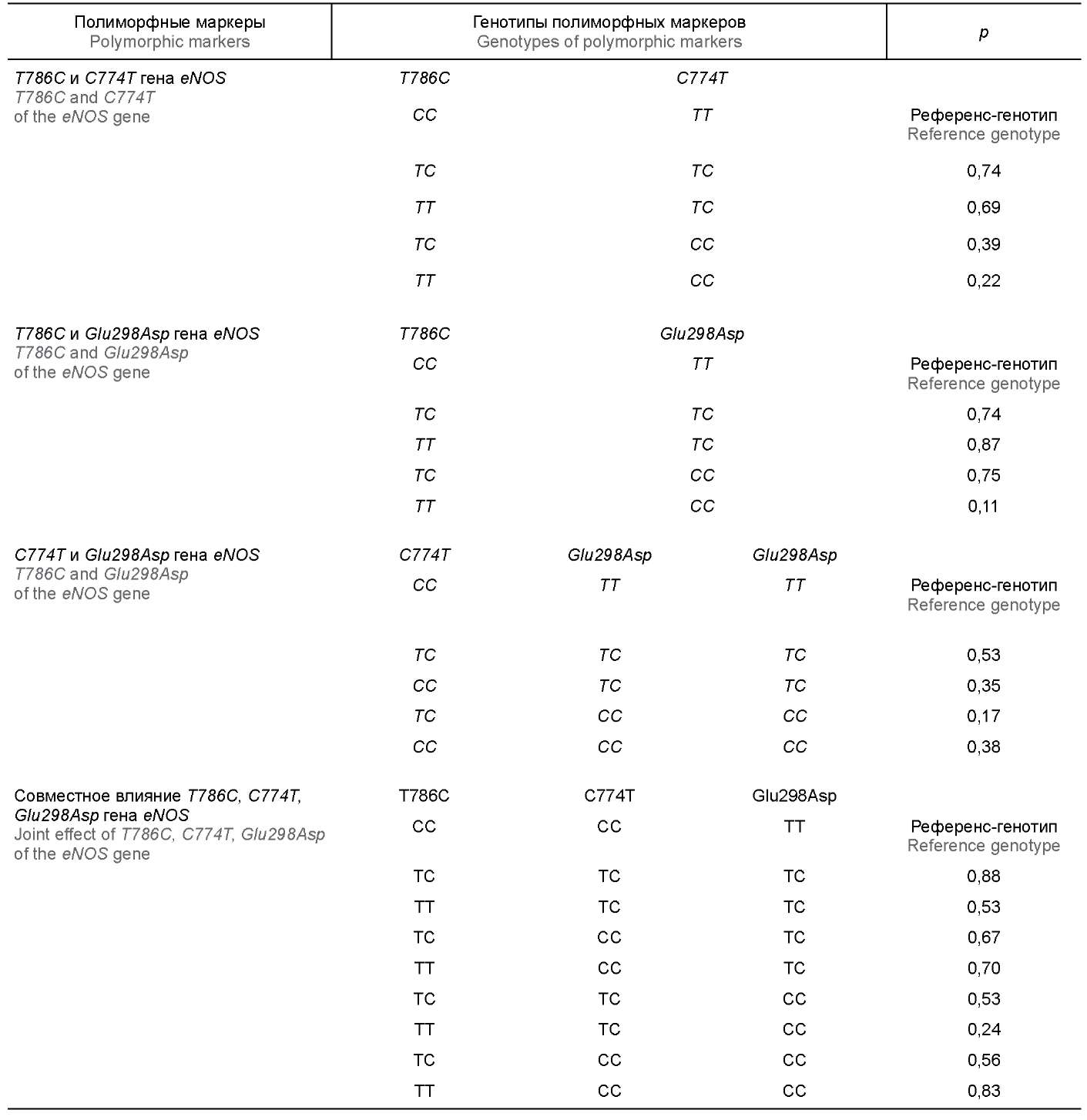
Материалы и методы. В качестве материала была использована периферическая кровь 93 пациентов с ПОУГ и 96 пациентов с катарактой. Сначала выделяли ДНК, затем проводили полимеразную цепную реакцию в режиме реального времени. Частоту встречаемости аллелей и генотипов в исследуемых группах рассчитывали при помощи критерия χ2 и точного критерия Фишера. Статистически значимыми были приняты результаты с p < 0,05. Для количественной оценки связи между возникновением ПОУГ у пациентов и носительством неблагоприятного полиморфного маркера были рассчитаны отношение шансов и 95% доверительный интервал.
Результаты. Среди маркеров С774Т и Glu298Asp не выявлено достоверных различий в распределении генотипов и аллелей гена eNOS. Установлены повышение частоты встречаемости гомозиготного генотипа ТТ; снижение встречаемости аллеля С по полиморфному локусу T786C гена eNOS у пациентов с ПОУГ.
Выводы. Полиморфные маркеры гена eNOS могут рассматриваться как факторы, влияющие на вероятность возникновения ПОУГ.
 54-62
54-62


Анализ заболеваемости людей бруцеллёзом и молекулярно-биологическая характеристика изолятов Brucella melitensis на длительно неблагополучных по бруцеллёзу территориях юга европейской части России
Аннотация
Введение. Для совершенствования эпидемиологического надзора за бруцеллёзом в России необходимы подробный анализ заболеваемости и изучение особенностей штаммов бруцелл, циркулирующих на территориях страны, где отмечается стойкое эпизоотолого-эпидемиологическое неблагополучие по бруцеллёзу.
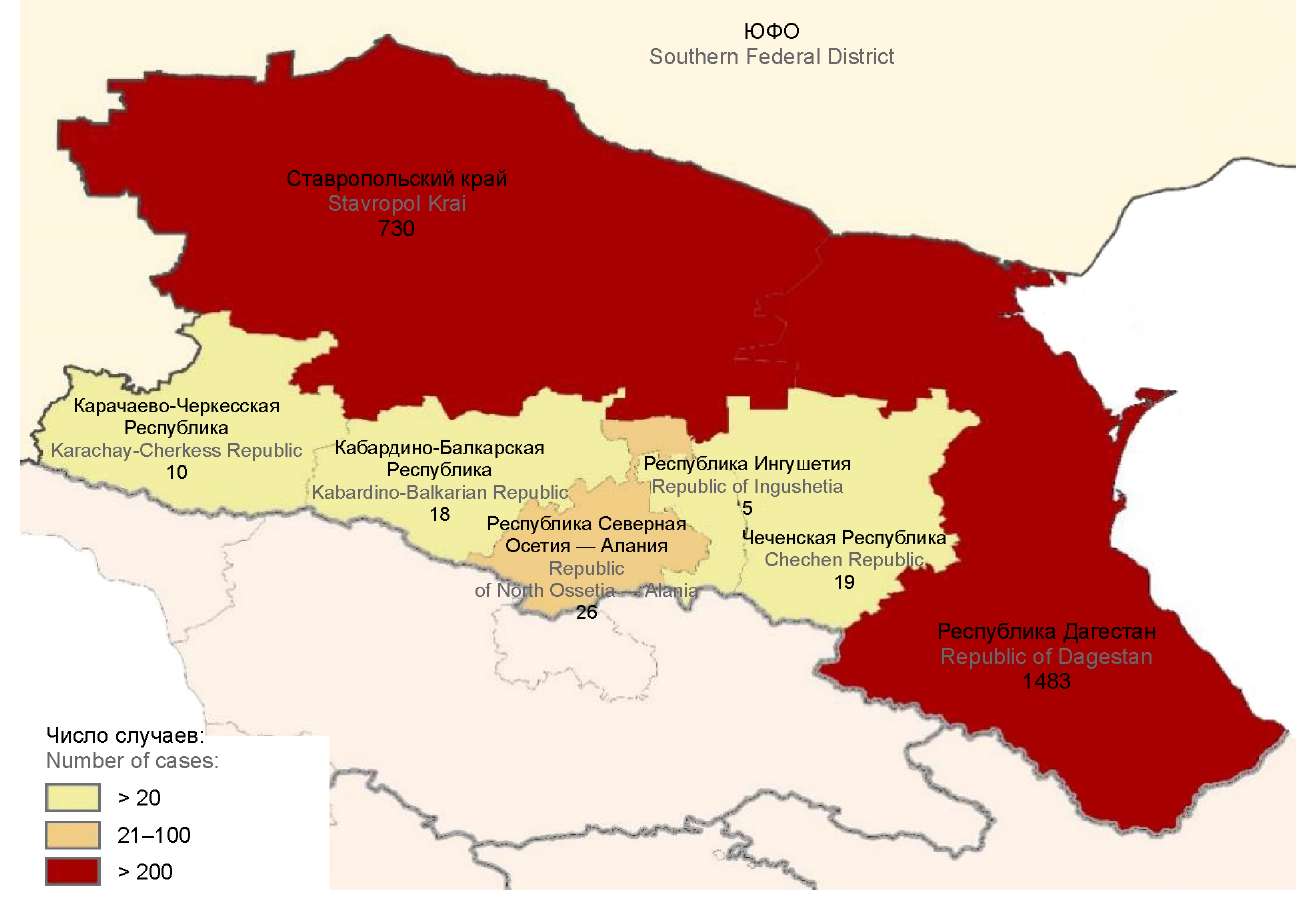
Цель исследования — изучение современных особенностей эпидемического процесса бруцеллёза и молекулярно-биологический анализ изолятов бруцелл на территории длительно неблагополучных по бруцеллёзу субъектов Южного (ЮФО) и Северо-Кавказского (СКФО) федеральных округов — Республики Дагестан (РД), Республики Калмыкия (РК) и Ставропольского края (СК).
Материалы и методы. Анализ заболеваемости бруцеллёзом в СКФО и ЮФО проводили на основе данных Управлений Роспотребнадзора за 2011–2020 гг. Изучено 56 культур Brucella melitensis, выделенных в 1999–2019 гг. от заболевших бруцеллёзом, постоянно проживающих на территориях РД, РК и СК.
Результаты. Ключевой фактор, способствующий возникновению случаев заболевания людей бруцеллёзом на территории юга европейской части России, — сохранение в регионе стойкого эпизоотического неблагополучия по бруцеллёзу мелкого и крупного рогатого скота. К ведущим сопутствующим факторам можно отнести: наличие в регионе «скрытых» эпизоотических очагов, неконтролируемых объектов производства пищевой продукции животноводства и её нелегальную реализацию населению, несанкционированное перемещение животных и животноводческих грузов, несвоевременную сдачу (передержку) больного скота. Результаты молекулярно-биологического анализа штаммов B. melitensis указывают на циркуляцию смешанной популяции бруцелл, в целом характерной для всего региона, без выраженной приуроченности изолятов к отдельным административным территориям. Вместе с тем всю изученную выборку штаммов можно условно распределить на две популяции (72 и 28% выборки), различающиеся профилями MLVA-16-генотипов по вариабельности локуса Bruce 19, что позволяет ассоциировать часть изученной популяции с территорией их выделения.
Обсуждение. Полученные данные позволяют научно обосновать возможность рассматривать длительно неблагополучные территории ЮФО и СКФО как единый (общий), стойкий и длительно активный антропургический эпизоотический очаг с циркуляцией смешанной, но характерной для региона популяции бруцелл.
 63-74
63-74


Влияние иммуномодуляторов на формирование поствакцинального противохолерного иммунитета
Аннотация
Введение. В связи с остающейся напряжённой ситуацией по холере в мире продолжаются создание профилактических препаратов и разработка способов повышения иммуногенности и протективности уже существующих вакцин против холеры. Сочетанное применение вакцин с иммуномодуляторами и цитокинами успешно применяется для специфической профилактики различных инфекций, в том числе и особо опасных.
Цель работы — экспериментальное изучение влияния иммуномодуляторов на иммуногенную и протективную активность вакцины холерной бивалентной химической с целью оценки возможности их использования для совершенствования специфической профилактики холеры.
Материалы и методы. Оценивали показатели клеточного и гуморального местного и системного иммунного ответа у экспериментальных животных, вакцинированных и получавших иммунотерапию, а также влияние иммуномодуляторов на протективную активность антигенов, входящих в состав вакцины холерной бивалентной химической.
Результаты. В ходе исследований выявлено, что применение иммуномодуляторов совместно с вакциной приводит к увеличению иммуногенных свойств антигенов. Иммуномодуляторы стимулируют дифференциацию CD4⁺-лимфоцитов, обеспечивая развитие иммунного ответа преимущественно по гуморальному пути, увеличивают количество В-лимфоцитов, антигенспецифических антителообразующих клеток, секреторного иммуноглобулина А в кишечнике вакцинированных экспериментальных животных. Иммуномодулятор глюкозаминилмурамилдипептид повышает протективные свойства антигенов, входящих в состав вакцины химической холерной бивалентной. Он наиболее эффективно защищал животных от генерализованной холеры.
Заключение. Использование иммуномодуляторов при противохолерной вакцинации, особенно глюкозаминилмурамилдипептида, может являться одним из подходов к совершенствованию специфической профилактики холеры.
 81-92
81-92


Оценка экономического ущерба, ассоциированного с заболеванием ветряной оспой детского населения Алтайского края
Аннотация
Введение. В современных условиях экономический анализ ущерба, наносимого ветряной оспой (ВО), приобретает особое значение, т.к. способствует принятию управленческих решений для достижения максимального медицинского профилактического эффекта.
Цель исследования — оценить экономический ущерб, наносимый заболеванием ВО детей 0–17 лет в Алтайском крае, для принятия управленческих решений.
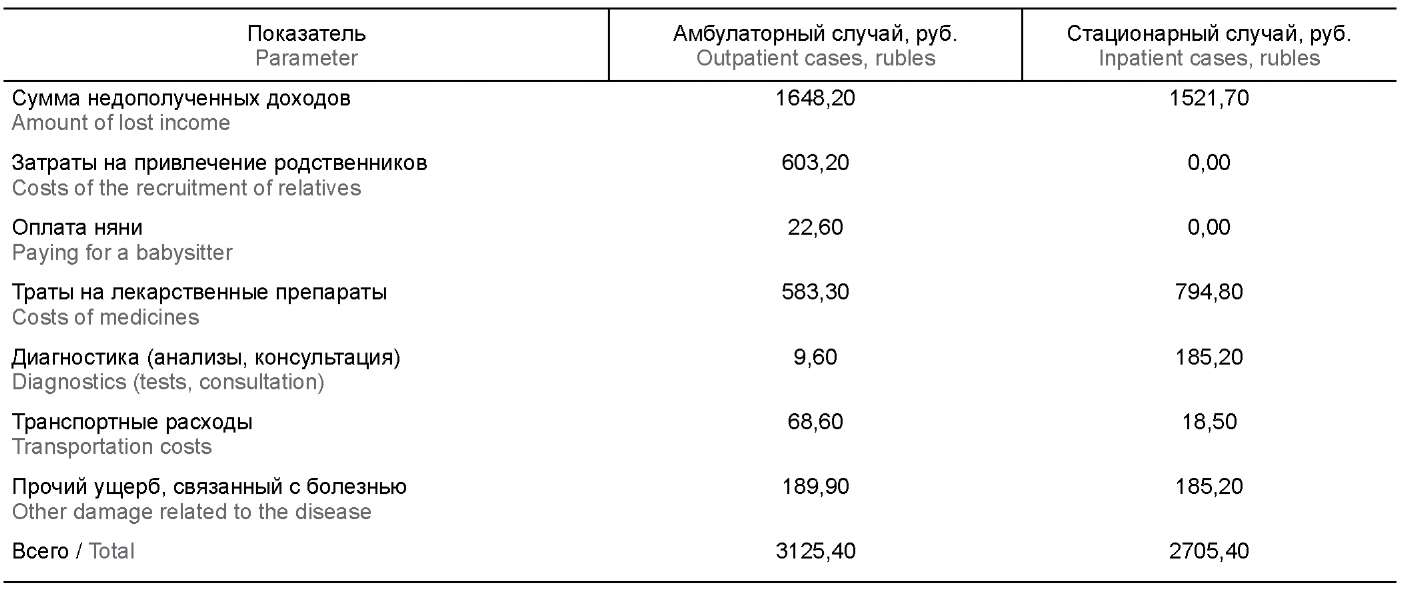
Материалы и методы. Для оценки затрат использовались данные по заболеваемости ВО, полученные в наших предыдущих исследованиях, тарифы Территориального фонда обязательного медицинского страхования для Алтайского края, данные о валовом региональном продукте, а также данные анкетирования родителей детей, больных ВО. Исследование проводилось на базе 2 поликлиник Барнаула (для амбулаторных пациентов) и детского инфекционного отделения Городской клинической больницы (для госпитализированных больных) за 1 календарный год (июль 2019 г. – июнь 2020 г.).
Результаты. Рассчитанный оценочный ущерб, наносимый ВО, за год в Алтайском крае составил 31 527 294,87 руб., из которого 42% — это затраты из собственных средств граждан (родителей детей, больных ВО). Затраты личных средств родителей на лечение одного амбулаторного случая ВО в среднем составили 3125,4 руб., а стационарного — 2705,4 руб.
Заключение. Расходы правительства и граждан Алтайского края на лечение ВО очень велики, и заболевание не поддается контролю существующими профилактическими мерами, о чём свидетельствуют стабильно высокие показатели заболеваемости. В связи с этим точная оценка экономического ущерба необходима для правильного принятия управленческих решений по внедрению новых профилактических мер, в том числе вакцинации в Алтайском крае.
 75-80
75-80


ОБЗОРЫ
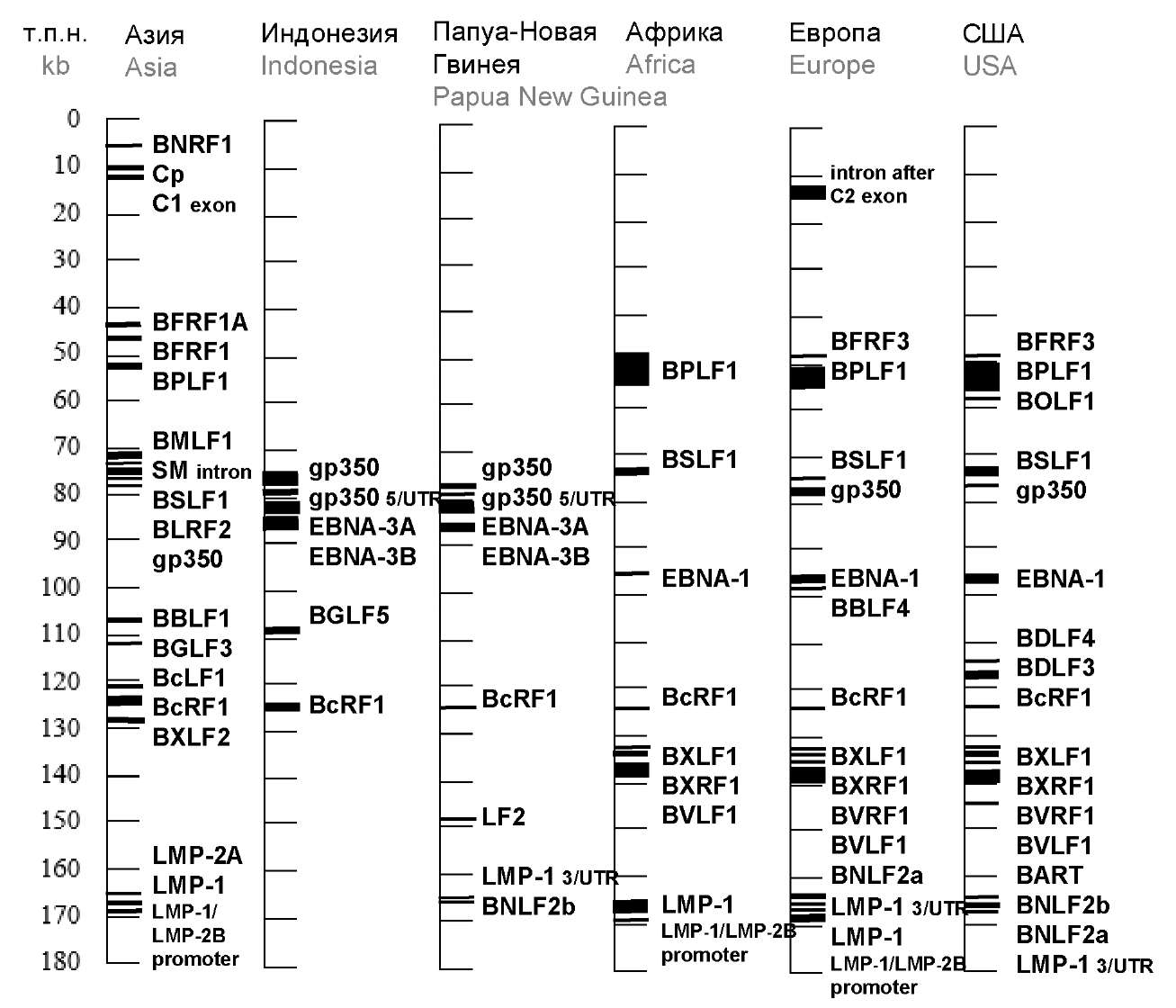
Генетическое разнообразие вируса Эпштейна–Барр: современный взгляд на проблему
Аннотация
В целом характеристика генетического разнообразия вируса Эпштейна–Барр (ВЭБ) лежит в основе изучения патогенеза, целевой разработки методов лабораторной диагностики, вакцин, средств специфической терапии ассоциированных с ним заболеваний, совершенствования системы эпидемиологического надзора за ВЭБ-инфекцией, а также дальнейшей детализации таксономии и классификации вируса. Целью настоящего обзора является обобщение и анализ данных литературы, посвящённых изучению генетического разнообразия ВЭБ, для перспективного развития методологии молекулярно-биологических исследований в клинической практике и эпидемиологическом надзоре за ВЭБ-ассоциированными заболеваниями. Работа выполнена на основе анализа публикаций, размещённых в базах данных PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, eLibrary. Отдельно сфокусировано внимание на изучении данного вопроса в России. Показано, что на протяжении нескольких десятилетий использовались подходы, основанные на анализе нуклеотидной и аминокислотной вариабельности отдельных генов ВЭБ или их участков. Однако единой, унифицированной системы, учитывающей все генетическое разнообразие ВЭБ, сильные и слабые стороны как более ранних, так и современных классификаций, не существует. Большинство публикаций посвящены изучению онкогена LMP-1. С развитием технологий полногеномного секвенирования возобновился поиск геновариантов и подтипов ВЭБ. На фоне динамичного развития данного направления выводы исследователей пока основываются на относительно небольшом количестве геномов, секвенированных с переменным качеством, проанализированных с применением разных биоинформационных стратегий, с неравнозначной выборкой с точки зрения географического происхождения; некоторые нозологические формы ВЭБ-ассоциированных заболеваний, географические области и этнические группы остаются неохарактеризованными. Развитие и оптимизация методических подходов на основе полногеномного секвенирования и секвенирования определённого набора генов будут способствовать расширению существующих представлений о генетическом разнообразии ВЭБ во всём мире, его связи с заболеваниями и, возможно, клиническими особенностями их течения, совершенствованию эпидемиологического надзора за ВЭБ-инфекцией.
 93-108
93-108


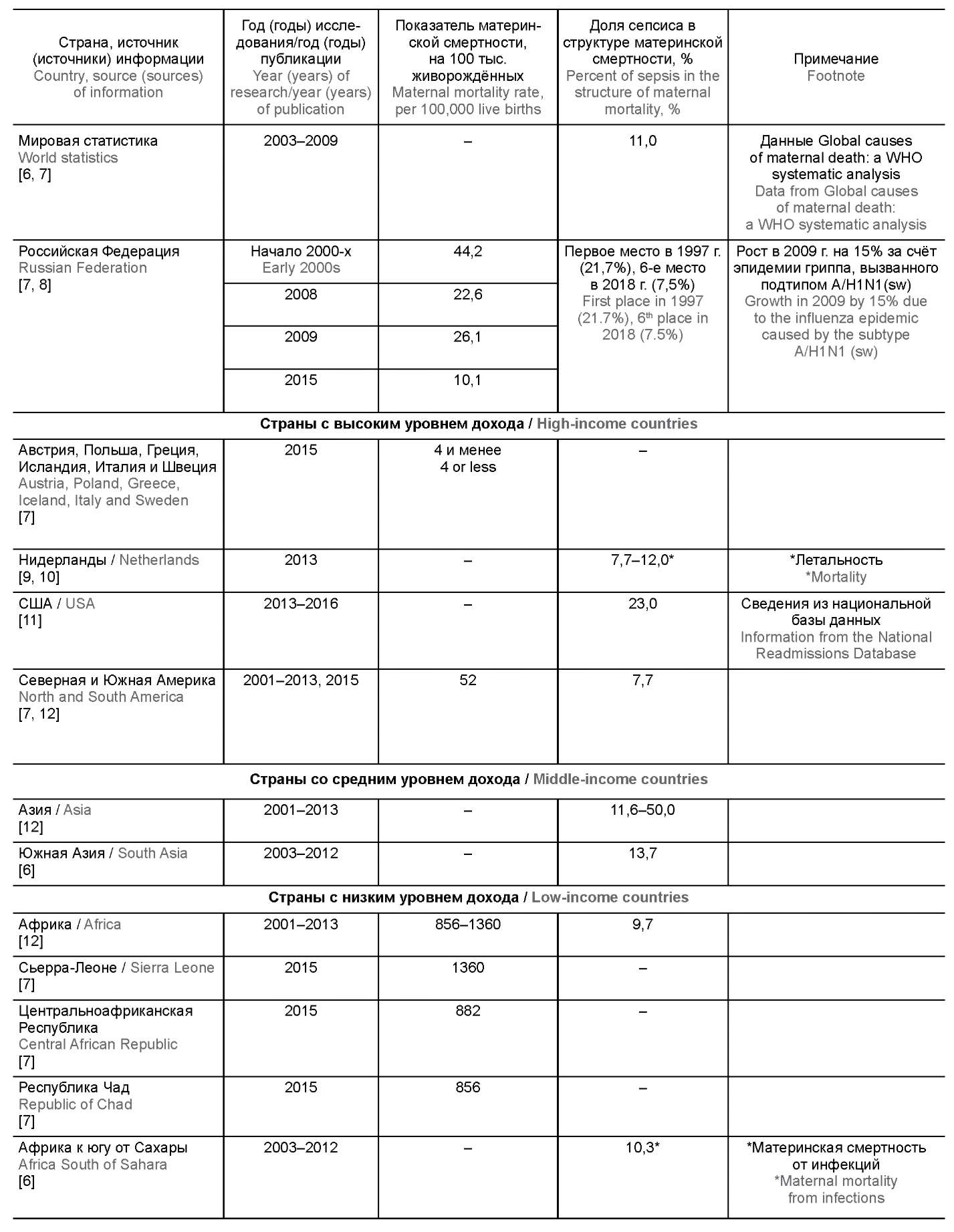
Гнойно-септические инфекции у родильниц. Часть 1. Распространённость, факторы риска, эпидемиологический надзор (обзор литературы)
Аннотация
Гнойно-септические инфекции (ГСИ) родильниц — одна из ведущих медико-социальных проблем современного здравоохранения. Значительная распространённость, тенденция к росту, недостаточная полнота их выявления и регистрации наряду с высокой степенью акушерской агрессии — вот современные черты данной группы инфекций.
Для изучения распространённости ГСИ послеродового периода (сепсис, перитонит, эндометрит, мастит и инфекции области хирургического вмешательства), выявления факторов риска и оценки эффективности эпидемиологического надзора за данными инфекциями был проведён анализ публикаций по этой тематике на нескольких информационных ресурсах: eLibrary, Google Scholar, PubMed, NCBI.
Установлено, что наиболее распространённой формой ГСИ родильниц является послеродовой эндометрит, на который приходится 3–20% случаев, а среди пациенток с послеродовыми воспалительными осложнениями — до 40,0–54,3%.
Одним из ведущих факторов риска развития ГСИ после родов является хирургическое вмешательство. Так, кесарево сечение увеличивает риск возникновения ГСИ на 5–20%.
Системы эпидемиологического надзора за ГСИ родильниц в разных странах имеют различия в подходе как к выявлению, учёту и регистрации случаев, так и к сбору сведений о месте и времени их наибольшего риска.
Таким образом, ГСИ родильниц являются динамически изменяющейся междисциплинарной проблемой на стыке акушерства, гинекологии и эпидемиологии. Несмотря на данные о распространённости отдельных нозологий и факторах их риска, существует ряд проблемных вопросов, которые могут быть предметом обсуждения и требуют решения.
 109-125
109-125


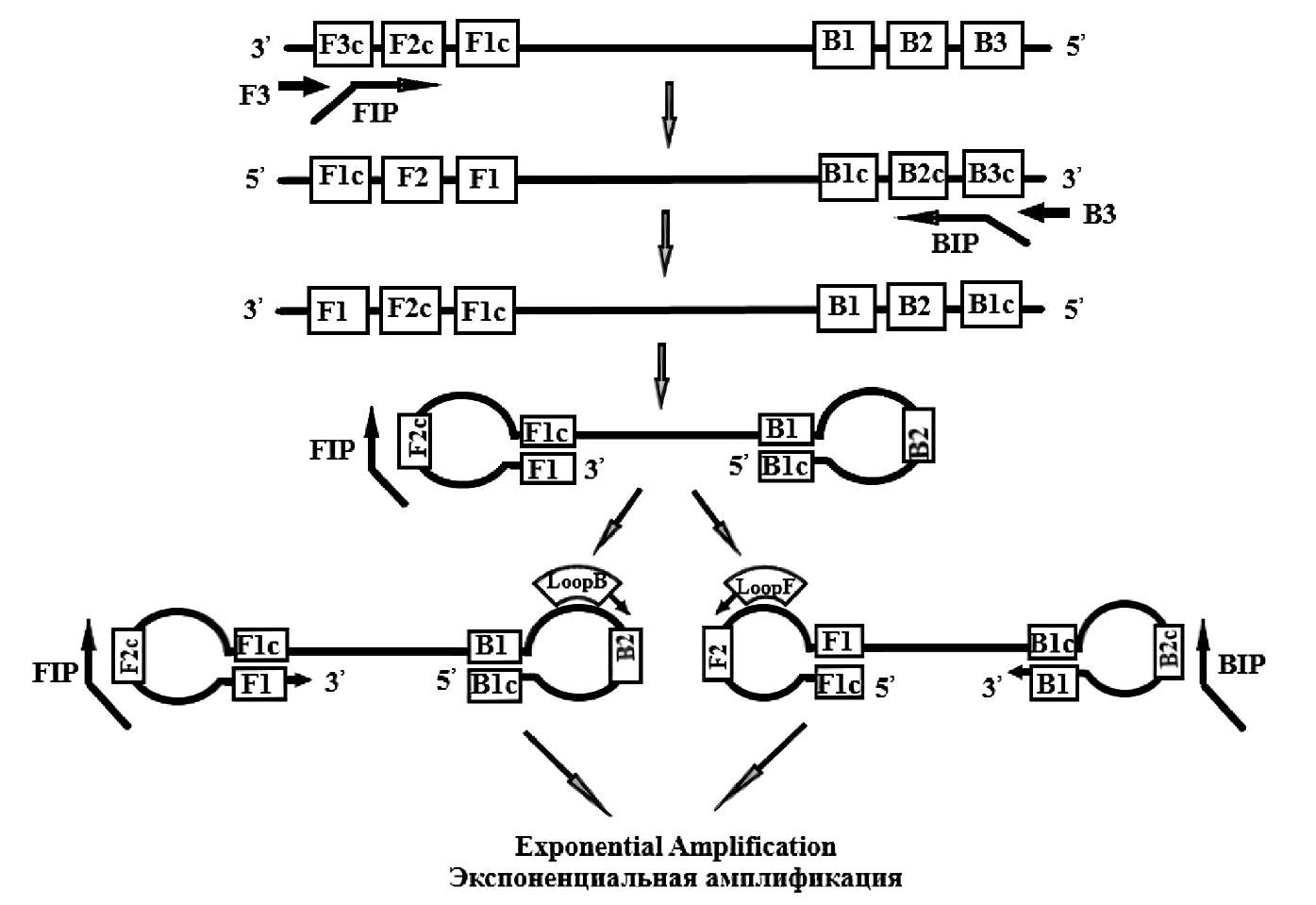
Сравнительный анализ методов изотермической амплификации нуклеиновых кислот
Аннотация
В обзоре рассмотрены и проанализированы методы изотермической амплификации нуклеиновых кислот, в частности петлевая изотермическая амплификация ДНК и РНК (LAMP/RT-LAMP), хеликазозависимая амплификация (HDA) и рекомбиназная полимеразная амплификация (RPA). Описаны преимущества и недостатки каждой технологии, оценена возможность их применения в молекулярной диагностике инфекционных болезней. Проведён краткий обзор литературы по использованию LAMP, HDA, RPA в диагностике вирусных, бактериальных инфекций и заболеваний протозойной этиологии. Показано, что метод LAMP имеет ряд преимуществ по сравнению с другими методами диагностики: высокую эффективность, специфичность, простоту, скорость постановки реакции и минимальные требования к приборному оснащению. Сделан вывод о том, что LAMP является перспективным методом в определении ДНК/РНК различных патогенов. Приведены данные о внедрении метода LAMP в диагностику особо опасных бактериальных и вирусных инфекций, в том числе для обнаружения РНК новой коронавирусной инфекции (SARS-CoV-2) в клинических образцах.
 126-138
126-138


ХРОНИКА
 139-140
139-140


НЕКРОЛОГИ
 141-142
141-142